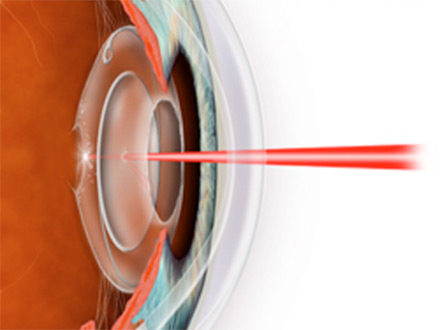
What is Neodmium YAG Laser Capsulotomy?
Only Nd: YAG (Neodymium: Ytrium-Aluminum-Garnet) laser is used for capsulotomy.
Trials have been made on CO2 laser and Nd: YLF (Neodymium: Ytrium-Lithium-Fluoride) laser.
INDICATIONS
The most common indication for Nd: YAG laser posterior capsulotomy is posterior capsule opacification, which reduces vision. (95%)
Other indications are obstructing the visualization of the fundus for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, monocular diplopia associated with PCO, and damming. The indications for anterior capsulotomy are capsular contraction syndrome, capsular block syndrome, GIL dislocation due to contraction of the edge of the capsulotomy.PCO is the most common visual impairment complication of cataract surgery in which the posterior capsule remains intact. (Around 50%)If capsular opacity does not explain the impairment of vision, care should be taken in terms of cystoid macular edema, which may be a complication of posterior capsulotomy.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Situations where the capsule is not seen, such as corneal scarring and edema, are the primary contraindications.
Those at risk of intraocular inflammation, CME, and retinal detachment are relatively risky.
Caution should be exercised in patients with uncontrolled glaucoma, noncooperative patients and patients who have difficulty sitting
Capsulotomy lenses can be used in patients with eye stabilization problems. If necessary, retrobulbar anesthesia can be applied.
APPLICATION
30 and 60 minutes before capsulotomy, apraclonidine is dropped by 0.5% to prevent post-operative TOP elevation.If capsulotomy lenses are to be used, topical anesthesia should be applied.
The patient can be dilated. It is possible to do without it. Short acting agents are used for dilatation. Before being dilated, the visual opposite of the procedure should be determined. For example, if the pupil is decentralized, a capsulotomy is opened in the appropriate area. If the patient has full iridectomy, the location of the capsulotomy is decided according to the upper eyelid margin and other anatomical structures. Before dilatation, the posterior capsule area that fits the pupillary rim can be marked.
After dilatation, the posterior capsule is examined and stress lines, opacities and adhesions are determined. According to thicker and thinner areas in the capsule, the energy to be used in the processes to be applied in those areas is changed. Generally, a 2-4 mm diameter capsulotomy is sufficient. If it is small, there may be glare and a decrease in contrast sensitivity. Larger capsulotomy is required in patients in whom fundus periphery should be seen.Abraham and Peyman lenses can be used as capsulotomy lenses