What is Keratoconus?
Keratoconus is the thinning and tapering of the corneal layer resulting in a cone shape. Cone shaped cornea causes poor vision in patients and decreased vision that cannot be corrected with glasses. Keratoconus patients complain that they get different degrees of glasses from every ophthalmologist they visit. Generally, corneal topographic maps made after the patients do not benefit from the glasses reveal the disease. It is present in patients who have no complaints, but who apply for laser treatment, and those identified after corneal examinations and cornea maps. In addition, it is a disease that occurs in patients whose cornea is extremely thinned after LASIK surgery.
The first sign of keratoconus is blurred vision. In addition, increased sensitivity to light, decreased night vision, headache, reading difficulties, and diplopia are common findings of the disease. Keratoconus is a disease that usually affects both eyes, but one eye may be more affected than the other and the patient feels as if they have only one eye disease. Keratoconus is often noticed in adolescence, rarely in the twenties or later. Astigmatism, which changes and increases at every eye examination, should bring to mind keratoconus disease.
If the disease is left without follow-up, there will be excessive thinning of the cornea (severe keratoconus), and the patient's vision is greatly reduced due to edema and turbidity
How is CCL Treatment applied?
Riboflavin (B2 vit) instillation
Before the procedure, the eye is anesthetized with topical anesthetic drops. After topical anesthetic drops, the corneal epithelium is mechanically removed with a blunt spatula. Riboflavin solution is dropped on the cornea, where the epithelium has been removed, 2 drops in 3 minutes intervals for 30 minutes. Riboflavin solutions developed in recent years can be applied without removing the epithelium.
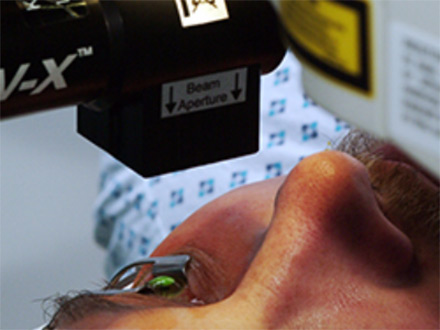
Application of UV Light:
After 30 minutes, the patient is seated on a biomicroscope. After the riboflavin fluorescence is seen in the anterior chamber, the patient is taken back to the operating room. 370 nm UV is applied in an area of approximately 7 mm at a distance of 4-5 cm from the corneal surface for 30 minutes. During the UV application, 2 drops of Riboflavin are dropped every 5 minutes. Bandage contact lenses are placed on the eye after the procedure, the eye is not closed.